
All that time thinking of a great topic, organizing your blog post, writing it (either with or without AI assistance), and finally publishing it. Then announce it to your target audience via social media and other channels.
What happens when you leave out search engine optimization (SEO)? Well, 80% of your efforts might fly out the window.
Spend another hour or two to optimize your blog for SEO and it can make all the difference. With optimized blog content, you can expect:
- Considerably more website traffic
- Popularity for 6 months or more, and
- Rich snippets, assuming your amazing article has popular and valuable content
- Potential for AI inclusion
We’ve seen it happen! When the blog content is right, it is surprisingly easy to add some off and on-page SEO. Blog SEO can turn your post into something much bigger than you ever imagined. Here are some blog SEO tips!
Doing the keyword research
Doing proper keyword research and finding a primary keyword to optimize blog content is generally the first task to create an SEO-friendly blog post. When your post contains the right target keywords, it makes it easier for users to find your article.
SEO reasons for keyword research
Search engine bots are continuously scouring web pages gobbling up trillions of words a minute. These words are stored in their databases along with the web pages where they were found.
When there are thousands of searches on specific keywords, the search engine algorithm needs to decide which web pages or blog posts to display and in which order for every query. The display results and search engine rankings are derived from the keywords and related websites stored in its database.
Various SEO tools find the words being queried on search engines, how many people query them, and from which country they are searching.
When you conduct keyword research, you use those tools to find a focus keyword for your article, along with related keywords that appear in other articles that focus on your primary phrase. Your job is to outdo those other blog posts with optimal blog SEO and fantastic content. Backlinks help a lot too.
SEO keyword research guidelines and action
To do keyword research, start by creating a list of keywords related to your blog post topic. You can use tools such as Google’s Keyword Planner or SEMrush to help generate a list of relevant keywords.
Once you have your list, analyze the search volume, competition levels, and cost-per-click for each keyword. This will help you understand which keywords are worth targeting in your blog SEO strategy.
When adding a focus keyword to your article, try to avoid keyword stuffing. This is a process where the exact keyword phrase is used multiple times in relation to the length of the blog post. Keyword stuffing is considered abnormal by search engine crawlers and can cause penalties against the page.
An explanation of how to do thorough keyword research is outside the scope of this post. But you can find an in-depth blog post about keyword research that goes into a lot more detail.

Adding the blog title and headings
Everyone skims when they read. If your blog post is paragraph after paragraph but has no headings in-between to let your readers know where they are going, they can lose interest very quickly.
When you optimize your blog by adding a focus keyword in the blog post title and other keywords to match a user’s search intent, you’re halfway there to increase blog traffic.
If your post isn’t long enough to break up into headings – only a paragraph or two – forget about blog SEO and don’t bother reading on. Seriously. Blog posts that rank well need to be longer than a few paragraphs.
SEO reasons for headings
Search engine algorithms are programmed to recognize headings. They pay attention to the keywords in h1, h2, and h3 headings. They give those words extra “juice” for placement potential. Targeted keywords in the blog post title alone (h1) is the most important for optimal link juice, followed by h2, h3, and so on.
SEO heading guidelines & action
Unless your blog post is extremely long, the H1 head is the name of the post, h2’s are secondary sections within the new blog post, and h3’s are sub-sections within the h2’s. Sometimes h4’s are added when there’s a lot of information to cover. There are a few different strategies to use when creating headings in your post:
- One strategy is to frame the post itself using headings as an outline and then write the content, including targeted keywords.
- Other writers find it easier to initially create the headings without worrying about keywords. Later they go back and see if any keywords will fit in the headings and still keep them “honest”.
- Other writers just write what’s on their mind without regard to headings. Once complete, they add them in.
- Writers often change the post title several times, trying to make it both catchy and contain the focus keyword of the page.
Whichever style you choose, make sure your headings guide the reader so they know what to expect in the paragraphs of content after the heading.
Chunk your post with bulleted or numbered lists
Similar to headings, bulleted points and numbered lists are also helpful to let users skim and realize the important parts of the article. Users focus on them and decide if they are related to the information they are seeking.
SEO reasons for bulleted and numbered lists
Search engines recognize ordered and unordered lists (the technical name for numbered and bulleted lists), giving their content more link juice.
We’ve all seen rich snippets on google search results with questions and answers in a 1-2-3 format. Adding these to your post in areas where users are asking questions or outline points that can be answered by the search engine results pages for queries helps attract rich snippet displays.
SEO bulleted and numbered list guidelines & action
Use bulleted points and ordered lists when appropriate. Think of asking a question with 3 options as answers, or step-by-step instructions on how to do something with a list outlining 1, 2, 3, and 4 as the steps.Not all posts will have areas where these work, but always look for them and add them in the code as appropriate.

Treat images appropriately
Pictures make your post more attractive and promote feelings. And a picture can be worth a thousand words when it comes to explaining something. Use them for design, interest, attention, explaining something, or adding character.
SEO reasons to use images
Search engines expect at least one image for every blog post. Schema markup of blog posts will throw an error if no image is present, so this is quite important.
Photographic images can leave a path that shows where and when a photograph was taken. If stock images are used, this location information is removed. But if you take photos that were taken locally and you do not remove that information, algorithms can use it to improve local search results and show recency – how old the images might be.
Algorithms also pay attention to ADA guidelines. A sight-impaired individual cannot see what is in an image, but if you code it correctly, their browser will read what is in the image to them. The words in an image alt tag get extra link juice as a result.
Finally, the name of an image is the number one thing that helps it come up in image search. From image search queries, a user can click through to the website from where they were found. There are so many reasons to use and code images that help optimize your blog!
SEO image guidelines & action: Images should contain the following:
- Name the image – Naming the image appropriately. Think of what people might search on to find the image you show and name it that. If your company requires codes on images, that’s ok. Just add the name to it also. It’s best to use hyphens between words and keep it as short as possible while still naming it appropriately.
- Add an Alt attribute – Once uploaded to your website, add an alt attribute that further describes the image. The alt attribute is the tag that browsers read to those who are sight-impaired. Adding keywords to the alt attribute is helpful to optimize your blog, but should not be the primary goal.
- Resize large images – When adding any type of image, check the size and be sure to resize larger images. Using images that are too large make a web page load much more slowly, and fast page speed is important for SEO too.

Title tag, meta description tag, URL
The SERP (Search Engine Result Page) landscape is continually changing when it comes to the information displayed to the user after a query. AI and schema have played a big role in making the display as user-friendly as possible.
Interestingly, in finding an example for use in this post, we noticed, the content in the meta description in just one search query had numerous errors.
The point of the example below is to show the display on the SERP. However, to avoid direct conflict, we’ve underscored the incorrect information with black dots so as not to mislead you.
Example 1 – Standard organic listing on a Google search result page:
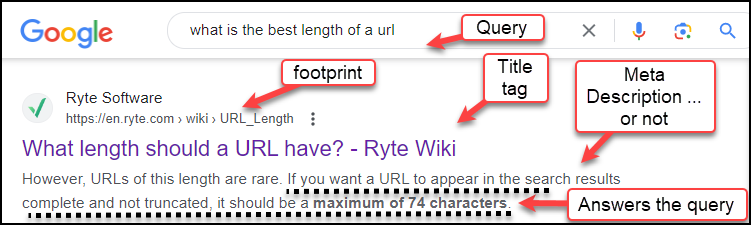
- Google’s standard display of this organic listing no longer shows the URL at all. How ironic that the listing description claims the URL won’t be truncated in search results if it is a certain length (dotted underline below). That’s how quickly things change! Bing still includes the URL in its SERP listings so at least for now, the results are still relevant.
- Search engines often pull content from the page rather than using the description tag that was written for the page (as in Example 2).
- The content in bold includes either the keywords in the query, or a phrase that answers the query’s question. “Maximum of 74 characters” is in bold below. This is an example of AI working for you.
Example 2 – Schema-enhanced organic listing on Google
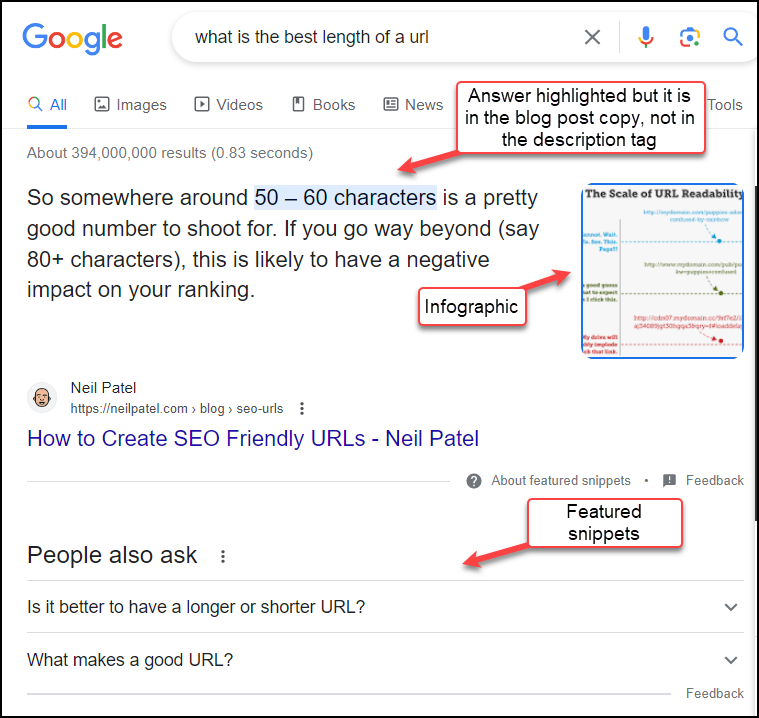
- The Google search result obviously reflects that Neil Patel’s post has the best answer to the query and has highlighted it with the answer highlighted, including a clickable snapshot of an infographic, the footprint navigation path on his site, and a clickable title tag.
- Additional featured snippets are below in the People also ask section.
- The listings in Example 2 are an example of Schema markup at work and its effect on increasing visibility. There has to be great content behind the schema, of course!
SEO reasons to optimize the title, meta description tag, and URL:
Search engines place considerable importance on words in a title tag (sometimes referred to as the meta title), but less so in meta descriptions and page names (URLs). Always pay attention to your title tag, and write a nice meta description tag so users know if your page is something they are interested in visiting.
The URL of a page can also provide some link juice from search engines because it presumably includes what the page is about. The amount of link juice garnered from a URL name seems to have dwindled over the last decade, but it still offers some benefits.
Title, meta description, and URL SEO guidelines & action:
There are specific guidelines that apply to each of these elements of your blog post. Since the browser title tag and meta description are usually what shows up on the SERP when a user performs a search, think of what might make a potential visitor click on your result vs. a competitor’s listing.
Title tag:
There are several SEO guidelines for the title tag.
- The browser title tag should NOT be the same as the post title. Make them unique, even if only one word is different.
- Despite all the warnings about title tag lengths, Google doesn’t penalize for tags that are too long. Other search engines do though. Some might not place pages–or even ban entire websites–if title tags are too long or short.
- There is a plethora of opinions about how long a title tag should be. We use a maximum length of 60 characters or less (spaces included) and a minimum of 30 characters.
- Include the page’s targeted keyword phrase in this tag. Algorithms give link juice to keywords in this tag.
- The tag should reference what is on the page. This is generally the keyword phrase or a part of it anyway.
- The tag should be written creatively, so a user will want to click on the link if they are interested in what your blog is about.
META Description tag:
- We opt for a maximum length of 160 characters and a minimum of 50 characters.
- Tags should include the page’s targeted keyword and/or variations of it.
- Like the browser title tag, the description tag should be regarded as a marketing element, something that entices the target market to click on the link above it.
URL:
- The URL or page name is something often forgotten when adding a blog post because most platforms make the URL the title of the blog post.
- This is often a big mistake because it can make the URL too long.
- Try to remove “stop” words such as: and, the, to, and so on to shorten longer URLs
- The recommended URL length (including everything before it) is 74 characters or less.
- Use hyphens as opposed to underlines in between words in a URL.

Internal links
Often blog post writers forget to include potential internal and external links. Links are quite important for SEO also.
If you are writing “cluster” posts about similar topics, it makes sense to link to other posts you’ve written about the topic that provides more detailed information about a specific item you mentioned. Users love being able to dig deeper if that is what they desire.
Users also want to be able to take action easily. If reading your post motivated them to purchase something right away, sign up for your service, or call you, adding appropriate links help them take their desired action.
SEO reasons to use internal links:
Search engines send link juice to any page your blog links to. The algorithms count up all the links that your blog post contains and divide it up into equal parts – at least at first.
So if you link to 5 pages, each page will receive one-fifth of the link juice from your page. This helps improve the chance that linked pages obtain higher search engine rankings.
Over time, search engines keep track of links that are actually clicked on by the readers of your post. If no users click on a link in your post, the receiving page stops receiving that link juice. This means you have wasted a portion of it.
Internal linking SEO guidelines & action: Be very careful and link to posts that have relevant and valuable content that users might wish to study further. Don’t overdo it, and don’t waste that valuable link juice.
Internal linking is also important to send users to your CTA pages. It is not helpful to you if they just read posts all day. You’d like them to act. So be sure to include links to CTA buttons or pages that lead them down the marketing funnel.
One warning is about taking internal linking too far. Users dislike too many links when they are trying to read something. They may get irritated and leave. Just something to keep in mind.
External links
Adding links that go to other websites is also important to optimize your blog.
Providing quality external links, especially when quoting data and its source, makes your blog posts more trustworthy.
SEO reasons for external links:
While you are sharing link juice outside your own website when linking externally, it is important NOT to be stingy. This is because your site also gets extra points from search engines for linking to other sites and will likely be penalized if you decide not to link anywhere else.
The quality of the sites you link to is quite important for blog SEO.
If your site links to high-quality sites, it will be rewarded by search engines. If it links to spammy sites or sites that have nothing to do with the topic or keywords it links to, it can be detrimental to both your site and the site to which it links.
Another reason to link externally is for “sharing” reasons. Your amazing article or blog post needs quality backlinks to help it get more visibility. When you start engaging with other bloggers, you may find similarities in topics and can then start sharing backlinks.
External link SEO guidelines & action:
Wherever your post cites numbers, figures, percentages, and so on, link to that quality source in the copy.
Try not to overdo it. If 3 or 4 data points come from the same source page, find a way to just link just one time to that page and creatively imply that what you documented in that paragraph came from that same source.
Schema markup
If you are not doing schema markup, this would be a good time to start. Many platforms include automated schema, but adding customized schema to your blog post makes all the difference. You can add a lot much more information so search engines understand your topic:
- References to Wikipedia or Wikidata about the topic
- Special markup for 1-2-3 steps
- FAQ markup when it answers specific questions
- Author, guest author, or people mentioned in the post
- A featured image you’d like to show in the SERP next to your post listing
- And much more
SEO reasons for schema markup
The number one reason to do schema markup is to get a better display on the SERP – rich snippets to be exact. Example 2 above shows how schema enhanced that SERP display. One article commands the top listing, and a large portion of it too.
Well-marked-up schema content is also more likely to be used in AI tools, which end up showing your content and reference to it in the AI chatbot results. Now how cool is that?
SEO schema markup guidelines & action
Unless you have an in-house team we highly recommend that you outsource this one. If that is not possible, at minimum do some research on high-quality plugins that will automate schema for you.
Top Of The List has been doing schema markup for many years. Contact us and watch your search results listing pop with features–literally begging visitors to click through to your post.

Perfecting
If you have the time, you can go a lot farther to perfect your SEO-friendly post. Look at Yoast or another good SEO plugin and see what they recommend about your specific post.
Grammatical issues that you might repeat over and over again can make the post harder for users to read or are just incorrect grammar. It’s good to check on yourself and see if you can improve. If it is a habit, no time like the present to recognize it and try to change it.
- Ways to include the targeted keyword phrase in more places. Some are just not possible, but it’s good to look.
- Add more “related” keywords to the post. Yoast or other tools look at the pages that are placing well on the keyword you wish to target and keep track of related keywords that are on the higher-placing sites. If you add those to your post, it may have a better chance of placing and beating your competitors.
Another way to perfect your post is to use a tool, such as SurferSEO to write your post and include the keywords necessary for placement. While beyond the scope of this article, it is surprising how many related keywords you will add to your post and the number of times they should be used. It literally counts them for you!
While this post may seem lengthy, optimizing your blog post is really quite easy once you do it a few times. In addition, the results will be amazing and well worth the effort.
Try it for your next 5 blog posts and then watch and wait as the number of visitors increases, showing a variety of different sources on-page optimization from which they came and increasing your overall conversions. You’ll be glad you took that extra time!
And if you don’t have that extra time, you know who to call. We’ll be glad to help!

Bev founded Top Of The List in 2006 and has over 25 years of experience working with technology. In her free time, she competes in dog agility competitions with her Golden Retrievers, Cosmo, and Finn.




